In July 2023, a study led by Professor Zhijian Xiao from Institute of Hematology and Blood Diseases Hospital, Chinese Academy of Medical Sciences & Peking Union Medical College was published in the international academic journal ——Blood Science . The title of the study is "Micheliolide exerts effects in myeloproliferative neoplasms through inhibiting STAT3/5 phosphorylation via covalent binding to STAT3/5 proteins". This study elucidates micheliolide (MCL) is a promising drug in combination with ruxolitinib for the treatment of MPNs.
Myeloproliferative neoplasms (MPNs) are clonal hematologic stem cell disorders characterized by excessive output of myeloid cells and an increased risk of leukemic transformation. Current management of MPNs is mainly focused on JAK/STAT signaling inhibition, with ruxolitinib being a cornerstone of treatment. However, a considerable number of patients have suboptimal responses to ruxolitinib, highlighting the need for alternative therapies. In this study, Xiao’s group evaluated the potential of micheliolide (MCL), a natural guaianolide sesquiterpene lactone, as a therapeutic agent in MPNs.
Xiao’s group conducted in vitro experiments using primary cells from patients with MPNs and JAK2V617F-mutated cell lines to investigate the effects of MCL on colony formation, cell growth, and survival. They also evaluated the efficacy of MCL in combination with ruxolitinib using JAK2V617F knock-in mouse models. Western blot analysis and molecular docking studies were performed to understand the molecular mechanism of action.
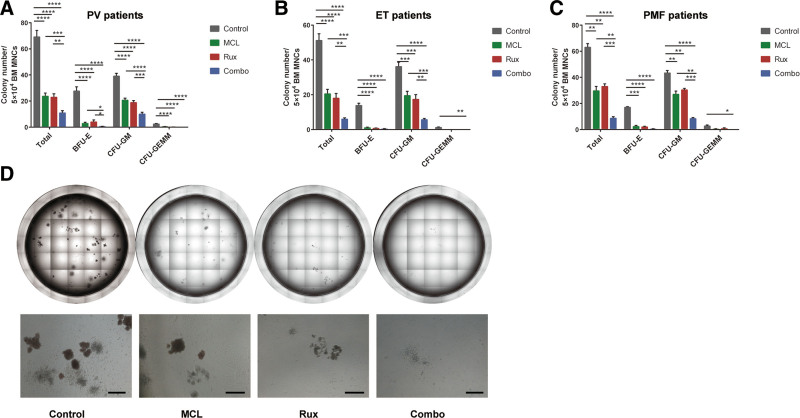
MCL alone effectively suppressed colony formation of hematopoietic progenitors and inhibited cell growth and survival of MPN cell lines in vitro. Co-treatment with MCL and ruxolitinib resulted in greater inhibitory effects compared to ruxolitinib alone. Moreover, an orally available derivative of MCL, dimethylaminomicheliolide (DMAMCL), significantly enhanced the efficacy of ruxolitinib in reducing splenomegaly and cytokine production in mouse models. Mechanistically, MCL can form a stable covalent bond with cysteine residues of STAT3/5 proteins, suppressing their phosphorylation and inhibiting JAK/STAT signaling. This study suggested that MCL is a promising drug in combination with ruxolitinib for the treatment of MPNs.
Reference:Huang H, et al., Xiao Z. Micheliolide exerts effects in myeloproliferative neoplasms through inhibiting STAT3/5 phosphorylation via covalent binding to STAT3/5 proteins. Blood Science. 2023 Jul 12;5(4):258-268.

