In May 2023, a study led by Professor Rong Fu from Tianjin Medical University General Hospital was published in the prestigious international academic journal —— Adv Sci (Weinh) (IF=17.521). The title of the study is " Immunogenic Cell Death in Hematological Malignancy Therapy ". The study introduce that the induction of immunogenic cell death (ICD) in hematological malignancies has shown promising results in enhancing the anti-cancer immune response.
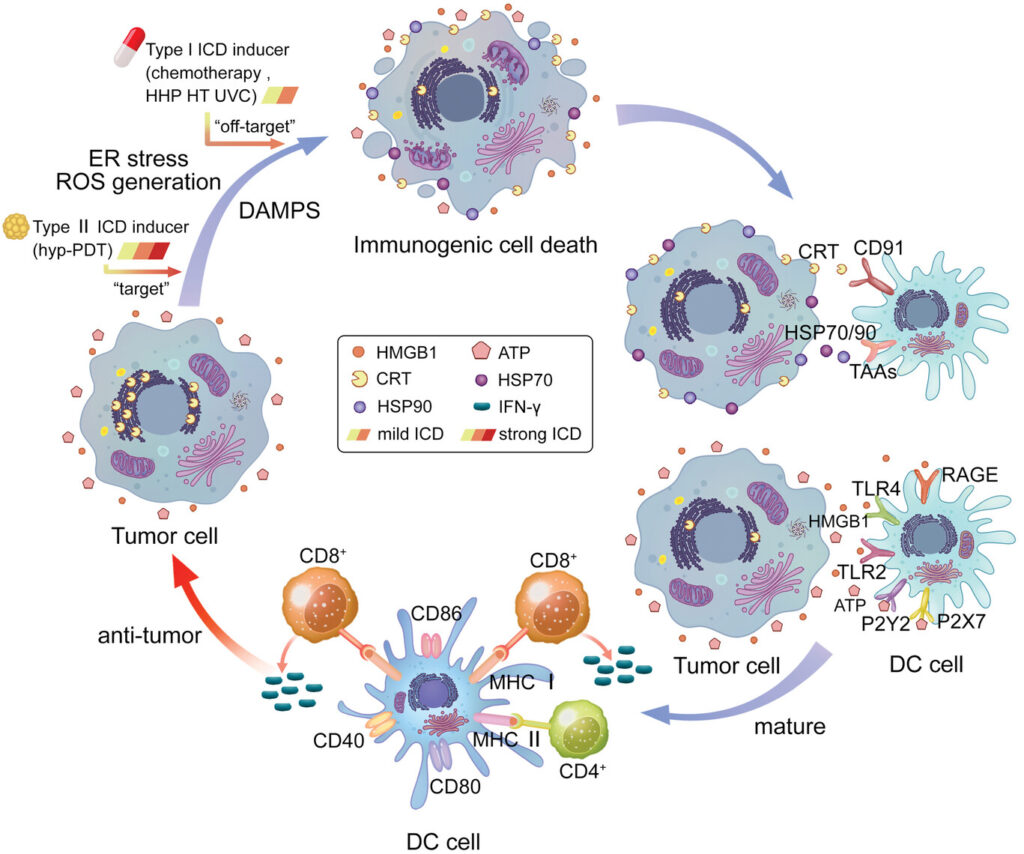
Hematological malignancies, including leukemia, lymphoma, and multiple myeloma, are characterized by abnormalities in the quantity and quality of blood cells. Immunogenic cell death (ICD) is a unique mechanism that triggers an intact antigen-specific adaptive immune response by releasing danger signals or damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs), making it a potential immunotherapeutic modality for the treatment of hematological malignancies.
(Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 May;10(13):e2207475.)
The purpose of this review is to summarize the existing knowledge about the induction of ICD in hematological malignancies and explore its potential for the treatment of these cancers. The review aims to provide insights into the mechanisms of ICD induction, the role of DAMPs and pattern recognition receptors (PRRs), and the combination of ICD inducers with other treatment strategies.
The review incorporates studies on hematological malignancies, ICD inducers, and the interaction between DAMPs, PRRs, and immune cells. Research data from various experimental models, including mouse models and in vitro studies, are included to support the findings.
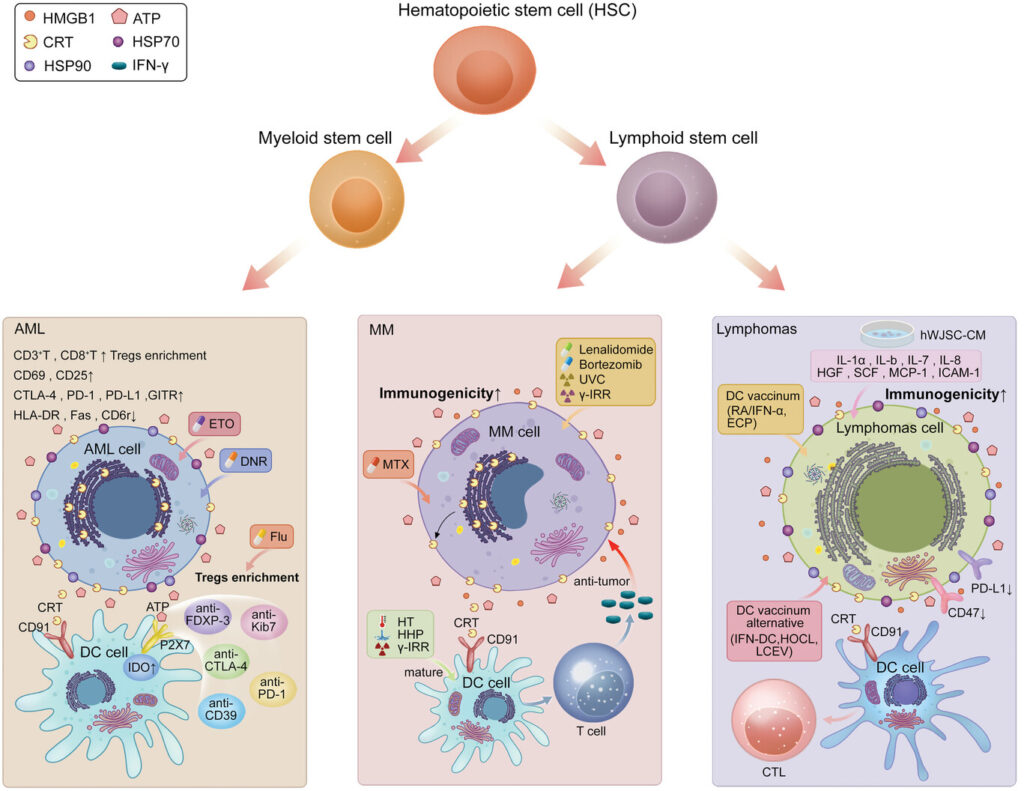
Several ICD inducers have been identified in hematological malignancies. Chemotherapeutic agents such as bortezomib and lenalidomide have been shown to enhance the immunogenicity of dead cancer cells and improve the ability of dendritic cells (DCs) to stimulate effector cells. Other inducers such as irradiation, high hydrostatic pressure, and hyperthermia have also demonstrated the ability to upregulate the maturation markers of DCs and produce antigen-specific T cell responses.
(Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023 May;10(13):e2207475.)
The studies reviewed indicate that ICD induction can enhance the anti-cancer immune response and improve patient outcomes in hematological malignancies. The release of DAMPs, such as calreticulin (CRT), adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and high mobility group box 1 (HMGB1), from dying cells stimulates the activation of DCs, leading to the presentation of tumor antigens and the activation of effector T cells. This immune response contributes to tumor cell death and disease control.
Understanding the induction of ICD in hematological malignancies is crucial for developing effective immunotherapeutic strategies. The findings outlined in this review highlight the potential of ICD as a treatment modality and emphasize the importance of combining ICD inducers with other treatment approaches to improve patient outcomes.
In conclusion, the induction of immunogenic cell death (ICD) in hematological malignancies has shown promising results in enhancing the anti-cancer immune response. Approaches involving various ICD inducers, including chemotherapy, physical cues, and targeted therapies, have demonstrated the potential to improve patient outcomes. Further research and clinical trials are needed to optimize the use of ICD in the treatment of hematological malignancies.


